Are you looking to improve your health and feel more energized but not ready to give up all your favorite foods?
A plant-focused diet is the perfect balance. It emphasizes eating more plant-based meals without requiring you to cut out animal products entirely.
This post will show you how to incorporate more plants into your diet, highlighting their health benefits and providing practical tips and delicious meal ideas to make the transition easy and enjoyable.
What is a Plant-Focused Diet?
A plant-focused diet emphasizes making plants the star of your meals while allowing flexibility for occasional animal products. It’s a sustainable, approachable way to improve your health without feeling like you’re giving up your favorite foods.
Unlike strict vegetarian or vegan diets, a plant-focused approach is all about balance. It encourages you to prioritize nutrient-rich foods like
- vegetables
- fruits
- whole grains
- nuts and seeds
- legumes
All while viewing animal products as optional or complementary. Think of it as a “plants first” mindset rather than an all-or-nothing lifestyle.
Why Choose a Plant-Focused Diet?
- Accessible for Everyone
This way of eating removes the pressure of eliminating entire food groups. Whether you’re a meat lover or just starting to explore healthier options, the plant-focused diet meets you where you are.
- Encourages Gradual Change
This diet doesn’t require an overnight overhaul of your eating habits. Start small by adding an extra serving of vegetables to your meals or swapping one animal-based meal a week with a plant-based alternative.
- Flexible and Sustainable
Flexibility makes this approach more sustainable in the long term. For instance, you might have plant-based breakfasts and lunches but enjoy a small portion of grilled chicken or fish at dinner.
- Focuses on Nutrient-Rich Foods
Plant-focused eating celebrates diversity. By prioritizing plants, you naturally increase your fiber intake, antioxidants, and essential vitamins and minerals while reducing saturated fats and processed foods.
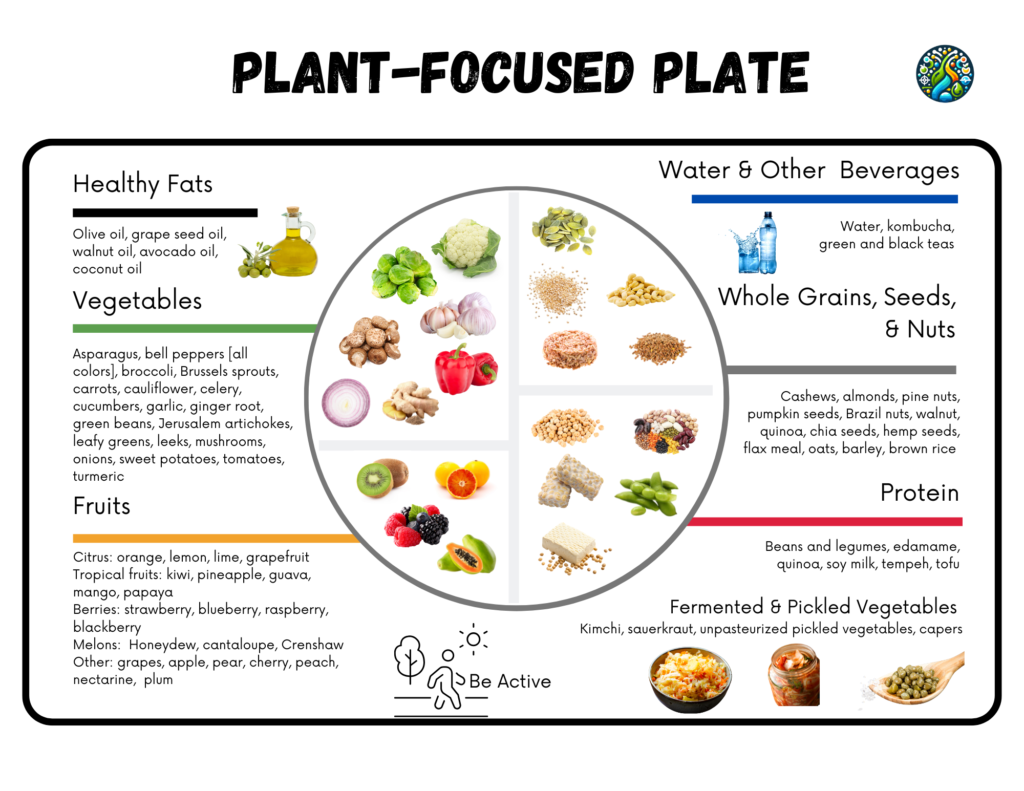
What Does a Plant-Focused Plate Look Like?
Think of your meals as 80% plants and 20% other ingredients. Here’s how a plant-focused plate might come together:
- Half Your Plate: Colorful vegetables (roasted broccoli, sautéed spinach, or a vibrant salad).
- A Quarter of Your Plate: Whole grains (quinoa, brown rice, or farro).
- The Remaining Quarter: A lean protein source, either plant-based (tofu, lentils) or animal-based (a small piece of grilled chicken or salmon).
- Add Healthy Fats: Drizzle olive oil over vegetables or sprinkle nuts and seeds on your salad.
Plant-Focused Diet vs. Plant-Based Diet
The terms might sound similar, but they differ in approach:
- Plant-Based Diet: Excludes all animal products, focusing entirely on plant-derived foods.
- Plant-Focused Diet: Highlights plants as the foundation but allows occasional animal products for flexibility and individual preferences.
By embracing this middle ground, you gain the benefits of eating more plants while maintaining the freedom to enjoy meat, dairy, or other favorites occasionally.
Health Benefits of a Plant-Focused Diet
- Better Heart Health
Plant-based foods like oats, beans, and leafy greens are low in saturated fat and high in fiber, which helps manage cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Improved Gut Health
The fiber in fruits, veggies, and legumes supports digestion and nourishes good gut bacteria. To boost gut health even further, add prebiotic-rich foods like garlic, onions, and bananas to your diet.
- Enhanced Brain Function
Healthy fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil, combined with antioxidants, protect your brain and support cognitive health as you age.
- Easier Weight Management
Plant-based meals are lower in calorie density, allowing you to enjoy satisfying portions while managing your weight.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Illnesses
Plant phytochemicals help protect cells, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of diseases like cancer and diabetes.
Strategies for Transitioning to a Plant-Focused Diet
Need help figuring out how to start? Here are some practical steps:
- Start Small
Swap one meal a day for a plant-based option. For example, try a fruit smoothie for breakfast or a hearty vegetable soup for lunch.
- Layer on Plants
Add more vegetables to dishes you already love. Toss spinach into pasta, mix beans into chili, or layer extra veggies on sandwiches.
- Meal Prep for Success
Batch-cook staples like roasted vegetables, grains, and hummus. Having these ready to go makes healthy eating quick and easy.
- Veganize Your Favorites
Use tofu or tempeh instead of meat in stir-fries, or swap cheese for nutritional yeast in pasta dishes. These small changes can make your meals more plant-focused without losing flavor.
- Stock Your Kitchen
Keep pantry staples like lentils, quinoa, and canned beans on hand. Fill your fridge with pre-washed greens, plant-based milk, and tofu for quick, healthy meals.
Utilizing AI tools like ChatGPT is also a great option for fine tuning your menu planning to fit into your lifestyle. Check out the Ultimate Guide to Nutrition AI prompts here. This guide is a great for actionable prompts to help you create personalized meal plans.

Nutritional Tips for a Balanced Diet
A plant-focused diet can be incredibly nutritious when carefully planned. Here’s how to ensure you’re meeting your dietary needs while enjoying the variety of plant-based foods:
Protein: The Building Block of Life
Plant-based proteins are abundant and versatile.
- Best Sources: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, nuts, seeds, and edamame.
- Quick Tip: Pair grains and legumes—like rice, beans, hummus, and whole-grain pita—to create complete proteins containing all essential amino acids.
Iron: Supporting Healthy Blood
Iron is essential for oxygen transport in the body.
- Plant-Based Sources: Lentils, spinach, chickpeas, tofu, blackstrap molasses, and pumpkin seeds.
- Enhance Absorption: Vitamin C boosts iron absorption. Add a squeeze of lemon to your lentil soup or pair spinach salad with orange slices.
Calcium: For Strong Bones and Teeth
You don’t need dairy to meet your calcium needs.
- Top Picks: Fortified plant-based milk, kale, broccoli, bok choy, almonds, tahini, and tofu made with calcium sulfate.
- Practical Tip: Blend kale into smoothies, and snack on roasted almonds or sesame-seed crackers with tahini dip.
Vitamin B12: Energy and Nerve Health
B12 is critical for energy and brain function but is typically found in animal products.
Vitamin D: Sunshine and Beyond
- Plant-Based Sources: Fortified cereals, nutritional yeast, fortified plant-based milk, and supplements.
- Tip for Plant-Focused Diets: Even if you consume some animal products, a B12 supplement can ensure adequate levels, especially for reduced meat consumption.
Vitamin D supports calcium absorption, immunity, and mood regulation.
- Sources: Sunlight exposure, fortified foods (e.g., plant milk, orange juice), and mushrooms exposed to UV light.
- Quick Tip: Spend 10–30 minutes outside daily, and include fortified foods during darker months.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Brain and Heart Support
Omega-3s are essential for brain health and reducing inflammation.
- Plant-Based Sources: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, hemp seeds, and algae-based supplements.
- How to Add Them: Sprinkle chia seeds on your oatmeal or blend walnuts into pesto for a healthy fat boost.
Zinc: Immune Support and Healing
Zinc helps maintain your immune system and supports wound healing.
- Plant Sources: Pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, lentils, quinoa, cashews, and fortified cereals.
- Boost Absorption: Soak or sprout seeds and legumes to reduce phytates and improve zinc availability.
Fiber: The Gut’s Best Friend
Fiber is essential for digestion and overall health.
- High-Fiber Foods: Whole grains, beans, lentils, berries, apples, carrots, and flaxseeds.
- Practical Tip: Replace refined grains with whole-grain versions like brown rice, quinoa, or whole-wheat bread.
Magnesium: Energy and Muscle Function
Magnesium supports energy production, muscle health, and nerve function.
- Sources: Spinach, pumpkin seeds, black beans, almonds, and dark chocolate (70% cacao or higher).
- How to Include It: Enjoy a handful of nuts or a square of dark chocolate as a snack.
Selenium: Antioxidant Protection
Selenium is vital for DNA synthesis and protecting against oxidative stress.
- Plant-Based Sources: Brazil nuts (just one provides your daily requirement), sunflower seeds, and tofu.
- Tip: Keep a small jar of Brazil nuts as a convenient snack for daily selenium.
Iodine: Thyroid Health
Iodine is critical for a healthy thyroid and metabolism.
- Plant Sources: Seaweed (e.g., nori, wakame), iodized salt, and fortified foods.
- Moderation: Be cautious with seaweed, as excessive iodine can impact thyroid function.

Delicious Plant-Focused Meal Ideas
Incorporating more plants doesn’t mean giving up on flavor. Here are some meal ideas to inspire you:
Breakfast
- Chia pudding with almond milk and fresh berries.
- Avocado toast with a sprinkle of chili flakes.
Lunch
- Chickpea salad wrap with fresh veggies.
- Mixed greens salad with roasted sweet potatoes, quinoa, and a small piece of grilled chicken.
Dinner
- Stir-fry with broccoli, carrots, tofu, and a light sesame sauce.
- Black bean tacos with avocado and salsa, paired with grilled shrimp.
Snacks
- Roasted chickpeas for a crunchy treat.
- Apple slices with almond butter and a dash of cinnamon.
Final Thoughts
A plant-focused diet is all about progress, not perfection. Whether you start with one plant-based meal a day or dive right in, every step helps improve your health and the planet.
Experiment with recipes (check out menu planners here), stock your kitchen with plant-powered staples and enjoy the journey to a healthier lifestyle—without giving up the foods you love.
In good health,
Steph
FAQs About Plant-Focused Eating
- Can I still eat meat and dairy?
Absolutely! A plant-focused diet is about balance. You can enjoy smaller portions of animal products while making plants the star of your plate.
- How do I avoid feeling hungry?
Focus on nutrient-dense foods like beans, whole grains, and healthy fats, which keep you full longer.
- Is this diet family-friendly?
Yes! A plant-focused diet’s flexibility makes it easy to adapt to different preferences. Kids can enjoy veggie-packed meals with familiar sides like cheese or chicken.
- How can I make plant-based eating affordable?
Buy bulk and focus on whole foods like beans, rice, and seasonal produce. Prepping meals at home also helps save money.
- What if I need more time?
Keep freezer-friendly options like veggie burgers and pre-cut vegetables on hand. Quick recipes like stir-fries and salads are perfect for busy days.
